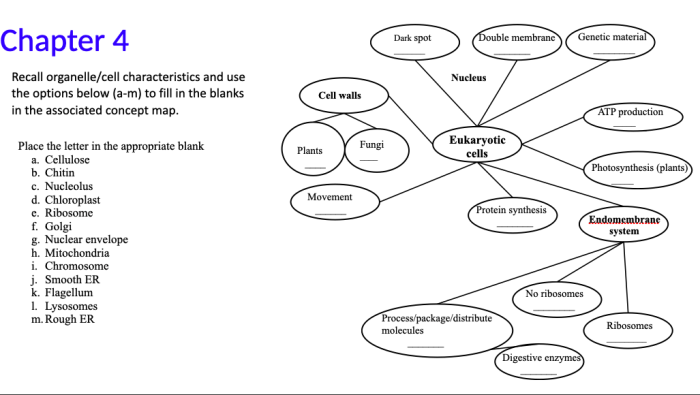
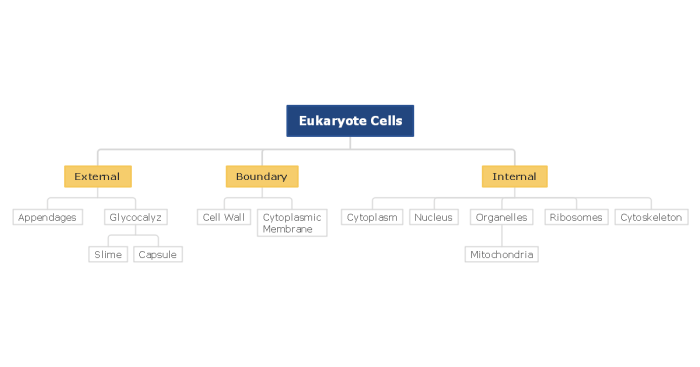
Eukaryotic cell components concept map embarks on a scientific odyssey, delving into the intricate workings of the eukaryotic cell, the fundamental unit of life for complex organisms. This comprehensive guide unravels the structure, functions, and interrelationships of the cell’s organelles, providing a roadmap to understanding the remarkable complexity and sophistication of cellular life.
From the protective cell membrane to the energy-producing mitochondria, each component plays a vital role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and executing the intricate processes that sustain life. Join us as we explore this fascinating realm, unlocking the secrets of the eukaryotic cell and gaining a deeper appreciation for the wonders of biology.
Eukaryotic Cell Components
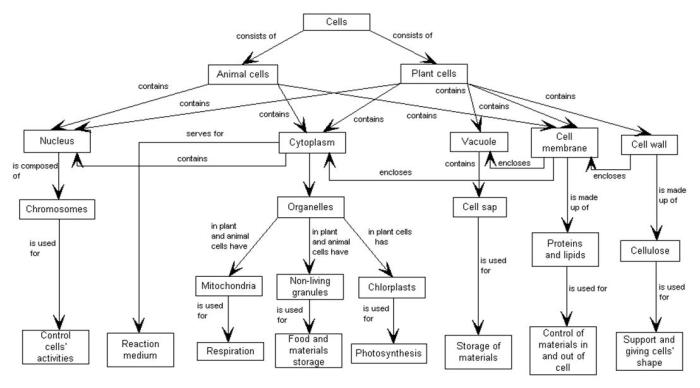
Eukaryotic cells are the basic unit of life for all plants, animals, fungi, and protists. They are characterized by a nucleus, which contains the cell’s genetic material, and a variety of other organelles, which perform specific functions within the cell.
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible layer that surrounds the cell and protects its contents. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, which is a double layer of phospholipids. Phospholipids are molecules that have a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-hating) tail.
The hydrophilic heads face outward, toward the water-based environment inside and outside the cell, while the hydrophobic tails face inward, away from the water.
The cell membrane is selectively permeable, which means that it allows some substances to pass through while blocking others. This is important for the cell, as it allows it to control the flow of materials into and out of the cell.
Functions of the Cell Membrane
- Protects the cell’s contents
- Regulates the flow of materials into and out of the cell
- Communicates with other cells
Components of the Cell Membrane
- Phospholipids
- Cholesterol
- Proteins
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance that fills the cell. It is composed of water, salts, proteins, carbohydrates, and other molecules. The cytoplasm is the site of many important cellular activities, including metabolism, protein synthesis, and cell division.
Functions of the Cytoplasm
- Supports the cell’s organelles
- Provides a medium for chemical reactions
- Stores nutrients
Nucleus, Eukaryotic cell components concept map
The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It is surrounded by a nuclear membrane and contains the cell’s genetic material, which is organized into chromosomes. The nucleus is responsible for directing the cell’s activities and for transmitting genetic information to new cells.
Functions of the Nucleus
- Directs the cell’s activities
- Transmits genetic information to new cells
Components of the Nucleus
- Nuclear membrane
- Chromosomes
- Nucleolus
Top FAQs: Eukaryotic Cell Components Concept Map
What is the purpose of a eukaryotic cell components concept map?
A eukaryotic cell components concept map provides a visual representation of the structure, functions, and interrelationships of the organelles within a eukaryotic cell, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of cellular organization and function.
How can I use a eukaryotic cell components concept map?
Eukaryotic cell components concept maps can be used as study aids, teaching tools, or reference materials to enhance understanding of cell biology. They can help visualize the complex relationships between organelles and their roles in cellular processes.
What are the key components of a eukaryotic cell?
Key components of a eukaryotic cell include the cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes, vacuoles, ribosomes, and cytoskeleton.