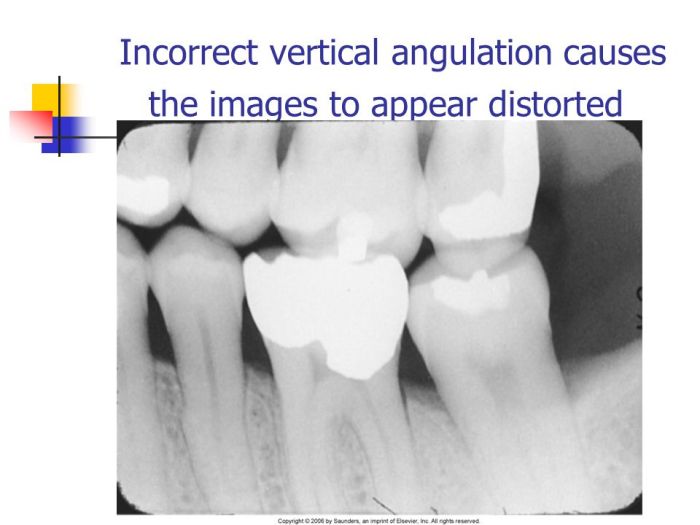
The result of incorrect vertical angulation takes center stage in this comprehensive exploration of its significance in dental imaging. This pivotal aspect of radiographic technique holds immense sway over diagnostic accuracy and subsequent treatment planning, rendering it imperative to grasp its nuances and implications.
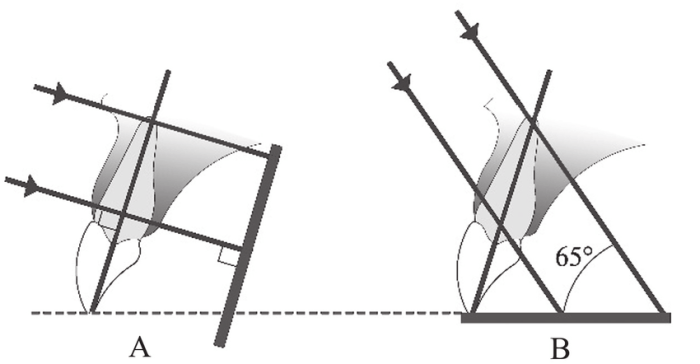
Vertical angulation, the angle at which the X-ray beam strikes the object being imaged, plays a pivotal role in producing distortion-free, diagnostically valuable images. Deviations from the optimal angulation can lead to a cascade of consequences, including image distortion, anatomical superimposition, and compromised diagnostic accuracy.
This article delves into the causes, effects, and techniques for achieving correct vertical angulation, highlighting its profound impact on patient care and treatment outcomes.
Definition and Explanation of Incorrect Vertical Angulation
Vertical angulation refers to the orientation of the X-ray beam relative to the long axis of the tooth. Correct vertical angulation is crucial for producing accurate and diagnostic dental images. Incorrect vertical angulation occurs when the beam is not perpendicular to the tooth’s long axis, resulting in distorted and misleading images.
Examples of incorrect vertical angulation include:
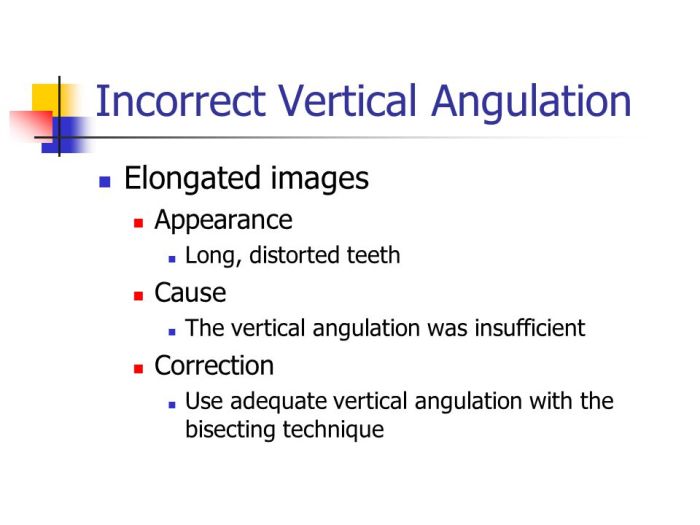
- Positive vertical angulation: The beam is tilted upward, causing the crown to appear elongated and the root to appear shortened.
- Negative vertical angulation: The beam is tilted downward, causing the root to appear elongated and the crown to appear shortened.
Incorrect vertical angulation can lead to misinterpretation of dental structures, incorrect diagnoses, and inappropriate treatment plans.
Causes and Effects of Incorrect Vertical Angulation, The result of incorrect vertical angulation
Incorrect vertical angulation can be caused by:
- Improper patient positioning
- Incorrect placement of the X-ray tube
- Malfunctioning equipment
The effects of incorrect vertical angulation include:
- Distortion of tooth anatomy
- Inaccurate assessment of periodontal bone levels
- Misdiagnosis of caries and other dental pathologies
- Ineffective treatment planning
Techniques to Correct Vertical Angulation
To achieve correct vertical angulation:
- Position the patient with their head parallel to the floor and the Frankfort plane perpendicular to the floor.
- Align the X-ray tube so that the central ray is perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth.
- Use angulation guides or other tools to ensure precise alignment.
- Adjust the X-ray tube head until the correct angulation is achieved.
Consistent and accurate positioning is essential for obtaining diagnostic-quality images.
Impact of Incorrect Vertical Angulation on Treatment Planning
Incorrect vertical angulation can lead to inaccurate treatment plans due to:
- Misinterpretation of caries extent
- Inaccurate assessment of periodontal disease severity
- Improper placement of dental restorations
- Ineffective endodontic procedures
Precise imaging is crucial for optimal patient outcomes and appropriate treatment decisions.
Guidelines and Standards for Correct Vertical Angulation
Industry guidelines recommend the following angulation angles:
- Maxillary anterior teeth: +5 to +10 degrees
- Maxillary posterior teeth: +10 to +15 degrees
- Mandibular anterior teeth: -5 to -10 degrees
- Mandibular posterior teeth: -10 to -15 degrees
Continuing education and training are essential for maintaining proficiency in vertical angulation techniques.
Troubleshooting and Common Errors
Common errors in vertical angulation include:
- Inconsistent patient positioning
- Incorrect alignment of the X-ray tube
- Equipment malfunction
- Misinterpretation of angulation guides
Troubleshooting steps include:
- Reposition the patient and realign the X-ray tube.
- Inspect the equipment for any malfunctions.
- Recalibrate the angulation guides.
- Consult with an experienced dental radiographer.
FAQ Section: The Result Of Incorrect Vertical Angulation
What are the common causes of incorrect vertical angulation?
Incorrect patient positioning, improper X-ray beam alignment, and variations in anatomical structures can all contribute to incorrect vertical angulation.
How does incorrect vertical angulation affect diagnostic accuracy?
Incorrect vertical angulation can distort anatomical structures, leading to misinterpretation and compromised diagnostic accuracy.
What are the steps involved in achieving correct vertical angulation?
Proper patient positioning, precise X-ray beam alignment, and the use of angulation guides are crucial for achieving correct vertical angulation.