News literacy lesson 3 bias – Embark on News Literacy Lesson 3: Bias, where we’ll dive into the fascinating world of media objectivity. In today’s digital age, it’s crucial to develop a keen eye for identifying bias in news sources, enabling us to navigate the vast media landscape with confidence and critical thinking.
This lesson will equip you with the tools to discern the subtle nuances of bias, ensuring that your news consumption is informed and balanced. By understanding the different types of bias, evaluating the credibility of sources, and fostering critical thinking, you’ll become an empowered news consumer, capable of making informed decisions about the information you encounter.
Identifying Bias in News Sources

Bias in news sources refers to the inclination or prejudice that can influence the reporting and presentation of information. Understanding and identifying bias is crucial for critical news consumption.There are various types of bias in news sources, including:
Confirmation Bias
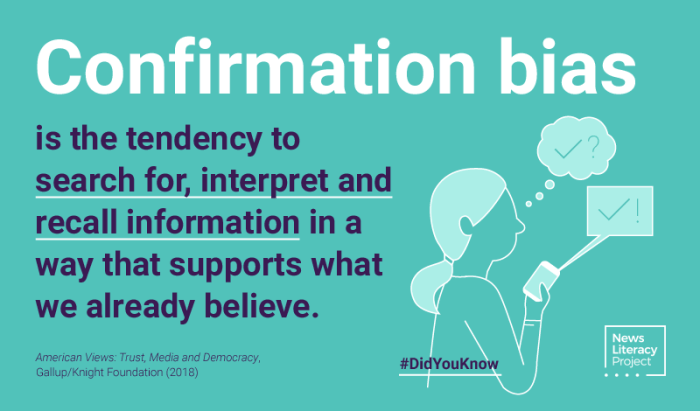
Confirmation bias is the tendency to seek and interpret information that confirms existing beliefs, while disregarding or downplaying evidence that contradicts them.
Omission Bias, News literacy lesson 3 bias
Omission bias occurs when relevant information or perspectives are intentionally or unintentionally left out of a news article, potentially shaping the reader’s understanding.
Framing Bias
Framing bias involves presenting information in a way that emphasizes or downplays certain aspects to influence the reader’s perception.Identifying bias in news sources requires critical analysis and attention to details. Consider the following techniques:
- Examine the language used in the article. Biased language often employs loaded terms, generalizations, or emotional appeals.
- Pay attention to the sources cited. Are they credible and unbiased? Are they presented fairly?
- Look for evidence of confirmation bias. Are only perspectives that support the article’s claims presented?
- Be aware of your own biases. Recognizing your own biases can help you identify and mitigate their influence on your news consumption.
By identifying and understanding bias in news sources, you can become a more informed and critical news consumer, able to make more informed judgments about the information you encounter.
Evaluating the Credibility of News Sources
Determining the reliability of news sources is crucial for informed decision-making. Several factors contribute to the credibility of a news organization, including its reputation, editorial independence, transparency, and adherence to journalistic standards.
News literacy lesson 3 emphasizes the importance of identifying bias in information. However, sometimes, it can be difficult to spot bias, especially when it’s cleverly disguised. For example, the phrase “te futueo et caballum tu” might appear innocuous , but it actually carries a derogatory meaning.
By understanding the techniques used to convey bias, we can become more discerning readers and better equipped to evaluate the credibility of news sources.
Evaluating Reliability and Trustworthiness
To evaluate the reliability and trustworthiness of a news source, consider the following criteria:
- Reputation:Research the reputation of the news organization by reading reviews and consulting media watchdog groups.
- Editorial Independence:Assess whether the news organization is independent from political or corporate influence.
- Transparency:Examine if the news organization discloses its funding sources and editorial policies.
- Journalistic Standards:Evaluate the news organization’s adherence to journalistic principles such as accuracy, fairness, and balance.
Examples of Credible and Non-Credible News Sources
Here are examples of credible and non-credible news sources:
| Credible Sources | Non-Credible Sources |
|---|---|
|
|
Understanding Media Literacy and News Consumption

In the digital age, media literacy has become crucial. It empowers individuals to critically analyze and evaluate the vast amount of information they encounter online, including news. Media literacy helps navigate the news landscape, making informed decisions about the credibility and reliability of news sources.
Responsible News Consumption
Responsible news consumption involves being aware of biases, evaluating credibility, and seeking diverse perspectives. By understanding media literacy, individuals can:
- Identify potential biases and conflicts of interest in news articles.
- Assess the credibility of news sources by considering their reputation, expertise, and transparency.
- Seek multiple perspectives and avoid relying solely on a single source.
- Verify information by cross-referencing with other reputable sources.
- Be mindful of their own biases and how they might influence their interpretation of news.
Addressing Confirmation Bias and Filter Bubbles
Confirmation bias is a tendency to seek out information that confirms our existing beliefs. This can lead to a distorted view of reality, as we may ignore or discount information that contradicts our views. Filter bubbles are created when algorithms personalize the information we see online, such as on social media.
This can reinforce our confirmation bias by limiting our exposure to diverse perspectives.
Overcoming Confirmation Bias and Filter Bubbles
To overcome confirmation bias and filter bubbles, we need to be aware of their existence and actively seek out diverse perspectives. This can involve reading from a variety of sources, talking to people with different viewpoints, and being open to changing our minds.
We should also be critical of information we encounter, evaluating its credibility and considering alternative explanations.
Fostering Critical Thinking and Discussion

Developing critical thinking skills is crucial for news literacy. It empowers you to analyze news articles objectively, form informed opinions, and engage in constructive discussions about current events.
To analyze news articles critically, ask yourself questions like: Who is the author? What is their perspective? Is the information supported by evidence? Does the article consider multiple viewpoints?
Engaging in Constructive Discussions
When discussing news, it’s important to:
- Respect differing opinions and avoid personal attacks.
- Listen actively to others’ perspectives and try to understand their viewpoints.
- Base your arguments on facts and evidence rather than emotions or assumptions.
- Be open to changing your opinion if presented with compelling evidence.
Answers to Common Questions: News Literacy Lesson 3 Bias
What are the different types of bias?
Bias can manifest in various forms, including political bias, corporate bias, cultural bias, and personal bias.
How can I identify bias in news sources?
To identify bias, pay attention to the language used, the selection of facts, the omission of relevant information, and the overall tone of the article.
Why is it important to be aware of bias in news?
Understanding bias allows you to evaluate the credibility of news sources, make informed decisions about the information you consume, and avoid being swayed by biased perspectives.